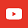
In 2023, the disclosed M&A deal volume of China’s new energy industry further increased to 784, reaching a new record high, and the disclosed deal value reached RMB220.4 billion.
After experiencing rapid growth and development in the past few years, the trend of transactions in the lithium battery industry has slowed down, and the deal value has fallen from its peak but still maintains a scale of over RMB75 billion.
Benefiting from multiple favorable factors such as power market reform, policy support, and improved project economics, both the deal value and volume in the energy storage sector have significantly increased. New types of energy storage technologies represented by sodium-ion batteries and liquid flow batteries have become the most capital-attracted tracks due to their complementarity with lithium batteries. Energy storage integrators focusing on industrial and commercial sectors remain a key area favored by capital.
Despite slowing capacity expansion, wind power and photovoltaic industry chains continue to attract investors due to gradual industrialisation of advanced technologies. Infrastructure investments such as wind and solar power stations are mainly focused on greenfield development; however, M&A transactions still maintained, driven majorly by: 1) continuous decrease in power generation cost; 2) under the background of accelerating integration between production and financing, state-owned enterprises gradually shift from leveraged buy-out through borrowings to using funds as carriers to participate in power station asset acquisitions; 3) non-energy SOEs focus on their core businesses while accelerating sales of power stations.


“With the rapid growth of lithium cell delivery volume year by year, the attention of capital has also expanded from manufacturers to upstream material suppliers. All kinds of funds have made layouts in lithium cell materials, expanding from cathode materials to anode and other auxiliary materials, from the mainstream technical route-related materials to the new technology route. In addition, domestic lithium cell manufacturers have begun to increase their efforts to make deployment in overseas capacity while stabilising the domestic capacity deployment. The financial pressure of investment and construction overseas and the policies of various countries have prompted domestic lithium cell enterprises to accelerate the expansion of overseas financing channels and introduce more overseas partners. At the same time, the lithium call industry is still in an intensive period of technological innovation. The process of material innovation and structural innovation around performance improvement and cost control continues to deepen, and the investment heat in solid-state batteries, silicon-based anode materials, and other fields has increased simultaneously. On the other hand, with the gradual increase in the average service life of installed lithium cells, cell recycling has attracted more attention, thus, more and more OEMs have begun to consider the construction and operation of recycling networks. ”
Highlights of M&A deals by sector
- The pattern of the battery manufacturing industry has become increasingly mature, with financing mainly for IPOs, private placements, and mergers and acquisitions of mature companies to further expand capacity and maintain a leading position.
- Financing for positive electrode materials and precursor-related enterprises still accounts for more than 80% of the overall transactions. The market will continue to explore the high density and cost-effectiveness of lithium iron phosphate positive electrode materials, as well as the ternary high-nickel cobalt-free route; in addition, early-stage capital attention is given to lithium-rich manganese-based materials with various performance advantages.
- Negative electrode materials: artificial graphite continues to consolidate its position as a mature negative electrode material through continuous integration and expansion; silicon-based negative electrode materials, which are considered as the main development route in the future, are accelerating commercialisation, attracting attention from financial and strategic investors focusing on early-stage investments in silicon-based negatives. Silicon-based material chemical companies enter into the negative electrode industry chain through across-industry acquisitions, jointly exploring continuous optimisation of related technologies and industrialisation
- The expectation for commercial landing of solid-state batteries is further strengthened while industrialisation accelerates; upstream materials such as solid electrolytes represented by solid-state batteries have also received attentions from capital markets.
- While lithium battery energy storage technology is dominant, the commercialisation of various new energy storage technologies such as sodium-ion batteries and flow batteries accelerates in 2023, attracting capital layout. Investment in sodium-ion batteries gradually extended from the cell to upstream material since 2022. With the continuous acceleration of downstream commercialisation, diversified development is emerging.
- The profitability of peak-valley arbitrage in energy storage has been fully demonstrated, and demand continues to grow explosively. In addition, with the demand for energy stability, security and ESG goals from industrial enterprises and industrial parks, ESS integrators are continuously sought after by capital markets.
- The source-side energy storage market will gradually shift from policy-driven to market-driven, making independent ESS a key player in front-end source-side markets.
- Photovoltaic production capacity iteration has gradually been implemented, with intense competition driving manufacturers to prioritise technological innovation and efficiency improvement, thereby creating new opportunities for the industry.
- The global photovoltaic market is expansive, and localisation policies are compelling Chinese manufacturers to expedite their global manufacturing layout.
- Offshore wind power has presented new opportunities, leading to the emergence of domestic equipment in the global market.
- The demand for wind and solar power station services is increasing, while digital energy management is entering a period of high demand.
- The integration of production and financing is intensifying, with funds playing a crucial role.
- Non-energy SOEs are prioritising their core operations, while the divestment of renewable energy assets is gaining momentum.
- In order to facilitate the transition towards low-carbon, high-quality development, local SOEs are actively investing in decentralised platforms that utilise regional resources to address the dual challenges of peak-valley substitution for on-grid electricity.
- The integration of solar power generation and energy storage holds significant potential as the most optimal solution.
- The focus of financing is gradually shifting from downstream fuel cells to the upstream of the hydrogen energy industry chain. The investment landscape is becoming more diverse and segmented, with early-stage financing continuing to dominate the hydrogen energy sector.
- Overall M&A value remains relatively modest, highlighting the need for increased confidence in the capital market for the hydrogen energy sector.
- Hydrogen energy companies are accelerating their global expansion efforts.